What Are The Types of Dental Implants?
Aug 05, 2024
The Types of Dental Implants
Dental implants are classified using a variety of methods, including categorization by number, fixation method, surgical procedure, material, implant system, etc.
In the previous article, we discussed various types of dental implants. Today, we will continue with our discussion.


Ⅰ Classified according to how fixed
The fixed support structure for implant-supported dentures differs from that of traditional denture restorations.
They can be categorized into fixed implant-supported dentures, covered implant-supported dentures, and removable partial implant-supported dentures based on the fixation method.
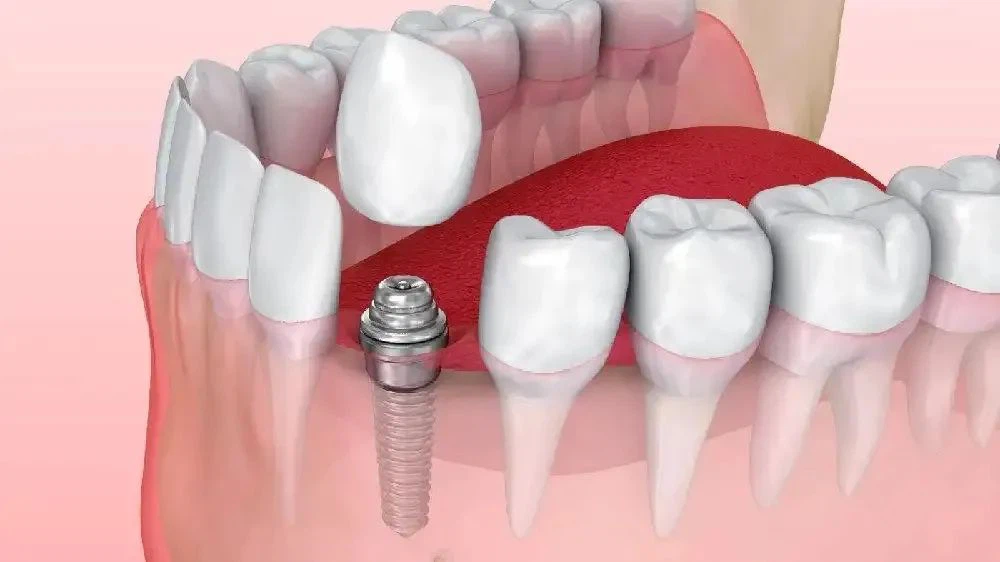
1. Fixed implant-supported dentures
Fixed dentures are a popular way to fix implants. The upper part of the implant-supported dentures is attached to the abutment using adhesive or screws. This restores the missing teeth's anatomical form and physiological function.
Patients cannot remove fixed dentures on their own after implantation. This method has a wide range of applications, closely resembling natural teeth, providing comfortable wear, strong fixation, and support.
This technique can be used to replace one or more missing teeth or even an entire dental arch.


2. Full arch (half arch) covered implant-supported Dentures
This type of implant-supported prosthesis is used in cases where there is severe bone resorption in the full arch (or half arch) due to tooth loss.
It is used in edentulous jaws that require 2 to 4 dental implants. Since the use of implants alone is not sufficient to support the fixed full-arch prosthesis in terms of stability and chewing function, and due to significant bone tissue absorption, a resin base is used to restore the missing bone tissue and improve facial aesthetics in this implant-supported prosthetic restoration.
In the case of full-arch covered implant-supported prostheses, the implant abutments can be designed with a variety of attachments, including clasps, bar attachments, ball caps, magnetic attachments, and sleeve crowns.
Covered dentures are essentially removable dentures in which the framework of the removable denture covers the roots, crowns, and implants and relies on these structures for support and stability. Patients can remove and wear them themselves, making them suitable for people with complete or extensive tooth loss.

3. Removable Partial Implant-Supported Dentures
This type of restoration is rarely used and is typically seen in cases where the implant placement has deviated from the original position or when there is an insufficient number of implants.
In situations where patients are unwilling or unable to undergo a complete reimplantation, the existing implants are used as support structures for removable partial dentures.
This approach is designed to eliminate the pain associated with the sinking of removable dentures.
The selection of the appropriate restoration method is particularly important based on the specific circumstances and extent of tooth loss. There are many factors to consider, and in future discussions, we will gradually analyze these factors.

Ⅱ Classified by Material
The implant is the part placed in the alveolar bone and is the only material placed in the human body during dental implantation.
Therefore, material selection is critical. Implant materials should be non-toxic, non-allergenic, non-carcinogenic, and non-teratogenic.
They should have good biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and excellent mechanical properties.
Dental implants can be classified based on their materials into metallic implants, ceramic implants, carbon implants, polymer implants, and composite implants.

1. Metal Materials
Since Branemark proposed the theory of osseointegration, pure titanium and titanium alloys have been the preferred materials for oral implants. Research has shown that pure titanium has excellent biocompatibility and corrosion resistance, as well as excellent mechanical properties, including hardness, tensile strength, yield strength, and fatigue strength. These properties meet the functional requirements of dental implants, and pure titanium has been widely used as an implant material in clinical settings with good restorative results.
Disadvantages: Despite the clinical application of pure titanium and titanium alloy implants, there are still limitations. Metal and its alloys have high strength, but their Young's modulus is relatively large, which leads to the stress shielding effect.

2. Ceramic materials
Mainly composed of materials such as zirconium oxide. Ceramics have an aesthetically pleasing appearance, with colors similar to natural teeth, and exhibit good biocompatibility. Scientists have explored the application of ceramics as implant materials in clinical practice. This class of materials is characterized by high mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, non-irritation, non-toxicity, and tissue compatibility.
Disadvantages: Long-term clinical data are still lacking for ceramic materials such as zirconia. Controversies exist regarding issues such as wear, crystalline degradation, crack propagation, and brittle fracture when used as dental implant materials.

3. Carbon Materials
This category generally includes materials such as glassy carbon and low-temperature isotropic carbon. These materials have relatively stable chemical properties and are not readily biodegradable. However, they are brittle and prone to discoloration.

4. Polymeric Materials
Common polymeric materials include acrylate and polytetrafluoroethylene. The chemical structure of these materials is similar to natural polymers found in the human body, making them more biocompatible.
However, further research is needed to investigate their strength and surface osteoconductive activity. In addition, they are susceptible to biodegradation, which may cause gingival irritation.

5. Composite materials
Composite materials typically combine various materials mentioned above to fully integrate their respective advantages and better meet the needs of the human body.

Ⅲ Classification by Implant System
Dental implants include various implant systems, including the Korean Dentium and Osstem systems, the Swedish Nobel system, the German Bego system, the American 3I system, the Swiss ITI system, and domestically produced systems such as Bacomed in China.
The brand of the implant has been the subject of much discussion in an earlier article-Which Is The Best Brand Of Dental Implants? Why?
Other classifications of implants will be discussed by Manners in the next issue.







